Sea freight Shipping from China
Obtain the most competitive shipping rate and send your goods with assurance.
Your Gateway to Unlocking China’s Opportunities
Now, you have a reliable partner who streamlines the process, offers both FCL and LCL shipping options, and delivers comprehensive, customized solutions designed to meet your specific requirements.

Traditional FCL and LCL Services
We provide both FCL and LCL sea freight services from China at unmatched prices.

Consolidating Orders from Multiple Suppliers
We enhance your company’s supply chain by merging shipments from various suppliers to maximize efficiency.

Warehouse Solutions
We offer efficient warehousing, inventory management, and order processing to enhance your supply chain.

Personalized Strategies
Our transportation solutions are customized to align with your unique needs.
What makes us the ideal partner for your sea freight from China?
We offer end-to-end supply chain solutions, including collection, consolidation, storage, order assembly, packaging, and distribution, ensuring effective inventory management, quality control, and timely order processing. Our emphasis is on prompt delivery while enhancing supply chain cost-effectiveness and operational performance.
Lowest Price Assurance
Our all-inclusive services enable us to design efficient shipping solutions and reduce costs.
Risk Minimization
Our expertise enables us to manage intricate customs procedures, reduce delays, and ensure seamless, dependable deliveries.
Optimized Operations
Our consolidation solutions merge multiple shipments into a single delivery, saving you both time and resources.
Reliable Partner
With our expertise, our supply chain team delivers strategic insights that extend past typical freight forwarding, providing you with confidence.
Enhance Supply Chain
Our all-encompassing services enhance efficiency, from managing suppliers and pickups to storage and final delivery.
Unlock Global Opportunities
Ship straight to your customers in your name, conceal supplier information, and safeguard your business confidentiality.
Grow with Assurance
We guide you through every phase of your business, providing the tools and resources needed to thrive.
Market Edge
Our efficient and compliant lithium battery shipping solutions provide you with a competitive edge in the rapidly growing electronics market.
Dedication to Your Shipments
We assume complete responsibility for every stage of the shipping process, guaranteeing your shipment arrives safely and punctually.
Sea Freight Knowledge Corner
What is China Sea Freight?
China sea freight refers to the transportation of goods via ocean vessels. Different types of ships and containers travel across the sea to deliver shipments.
The primary advantage is its low shipping cost, but it’s important to note that it’s one of the slowest shipping methods, which may not be ideal for time-sensitive businesses.
Comparison with Other Shipping Methods (Air, Rail, Road)
When compared to other methods like air, rail, or road shipping, sea freight has distinct characteristics.
-
Air Freight: Air shipping is fast and reliable, but it comes with a significantly higher cost. It’s particularly suitable for shipments weighing between 30 kg and 100 kg.
-
Rail Freight: Rail offers a middle ground in terms of speed and cost. It’s generally more affordable than air freight but faster than sea freight. However, China lacks rail infrastructure to reach all countries globally.
-
Road Freight: Road transport works best for domestic shipping, typically from one city to another. While China has limited road links to other countries, it can still be a viable option for specific regions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sea Freight
Sea freight can be a great choice depending on your needs. Here’s an overview of its pros and cons:
Advantages (Pros):
-
Cost-Effective: Sea freight is the most economical shipping option, with the lowest cost per kilogram of goods transported.
-
High Capacity: Ideal for shipping large volumes, sea freight can handle hundreds of containers at once, making it perfect for bulk shipments.
-
Global Reach: Sea freight connects China to ports all around the world, offering extensive international shipping options.
Disadvantages (Cons):
- Slow Shipping: One of the major drawbacks is the slow transit time, often taking 20-30 days or more for shipments to reach their destination, which can be problematic for businesses with urgent delivery needs.
Sea Freight Options: FCL and LCL
Sea freight typically offers two main options: Full Container Load (FCL) and Less than Container Load (LCL). Below is an overview of both options.
Full Container Load (FCL)
A full container load involves filling an entire container with goods of the required size. The standard container sizes are:
- 20GP (20-foot General Purpose Container): A container that is 20 feet in length, with a capacity of approximately 33.2 cubic meters. (Perfect for compact, heavier items or low-volume shipments. Offers exclusive use of the container. )
- 40GP (40-foot General Purpose Container): This container is double the size of the 20GP, with a capacity of 67.7 cubic meters.(Twice the size of the 20GP. Ideal for larger volumes of cargo.)
- 40HQ (40-foot High Cube Container): A variation of the 40GP, this container offers more height and a capacity of 76.3 cubic meters.(Provides extra height compared to the 40GP. Perfect for larger items that need more vertical space.)
Less than Container Load (LCL)
If your inventory doesn’t fill an entire container, LCL is the alternative option. With LCL, your goods are consolidated with others in a shared container. However, a downside is that the container will only be shipped once it’s filled. For example, if you have half the load for a 20GP container, the shipment will not proceed until it is fully packed.
Used when the cargo doesn’t fill a full container. The shipment is dispatched once the container is filled with goods from various shippers.
If you’re considering sea freight, there’s much more to evaluate. Here are the essential elements of ocean shipping.
Freight Forwarders
A freight forwarder is typically a company or individual responsible for shipping goods on behalf of the shipper. Think of them as intermediaries between the shipper and various transportation providers. With their expertise, the transportation of goods becomes streamlined and efficient.
Shipping Lines
Shipping lines are firms that operate vessels to transport goods between seaports. These companies often own and manage the ships, providing essential shipping services to customers. They play a key role in facilitating global sea freight operations.
Port Authorities
Port authorities are local organizations or governing bodies responsible for managing one or more ports. They regulate port activities, enforce rules, and oversee critical operations to ensure smooth and secure port operations.
Customs Brokers
A customs broker is a third-party agent who assists shippers with customs procedures. They help gather necessary documentation and expedite the customs clearance process, playing a vital role in international trade.
Central Chinese Provinces Facilitate Shipping from the Ports
Several key Chinese ports play a vital role in global shipping. Here are some of the top ports in China:
Shanghai
Shanghai Port is located in the Yangtze River Delta and is one of the busiest ports in the world. It serves as a critical hub for both container shipping and bulk cargo. The Port of Shanghai handles around 42 million TEUs annually.
Highest capacity in China.Major global hub, critical for China’s trade and logistics network.
Shenzhen
Shenzhen Port, situated in the southern part of the Pearl River Delta, covers more than 260 kilometers of trade routes. It is a major port for international trade, with an annual capacity of 27 million TEUs. The port supports container traffic from over 100 countries.
Remarkable ocean freight operations. Renowned for its streamlined processes. A major hub for manufacturing and export in the Pearl River Delta.
Ningbo-Zhoushan
Located on the East Coast across from Shanghai, in Hangzhou Bay, Ningbo-Zhoushan Port is the busiest for cargo shipments in China. This state-owned port processes 19 million TEUs annually and connects China to 90 countries.
Outfitted with state-of-the-art manufacturing technologies—helps alleviate pressure on other Chinese ports.
Plays a key role in reducing congestion at major ports.
Guangzhou
Guangzhou Ports, located along the Dongjiang, Beijiang, and Xijiang rivers, play a crucial role in connecting the industrial regions of these areas to global markets. With an annual capacity of 23 million TEUs, it streamlines cargo shipping to numerous countries.
Extensive storage facilities. Crucial for both domestic and global trade.
Qingdao
Qingdao Port, located on the Yellow Sea, has a significant global presence. With a capacity of 22 million TEUs, it links China to 130 countries and over 450 ports worldwide.
Center for advanced manufacturing operations. A vital port for Northern China, supporting its industrial infrastructure.
Tianjin
Tianjin Port, situated near Bohai Bay along the Haihe River, handles various types of containers, cargo, and passenger vessels. It has an annual capacity of 18 million TEUs and connects China to 180 countries and 600 ports globally.
Crucial for commerce with Northeast China and surrounding areas.
How to Choose the Best Port for Your Shipment
Don’t settle for an average port that might not meet your requirements. Here are some essential factors to consider when selecting the ideal port for your shipping needs.
Shipping Capacity
A port with high shipping capacity ensures you can ship even during peak times, preventing delays and ensuring timely deliveries.
Efficiency and Clearance
The efficiency of processing is key to speeding up your shipments. Low efficiency can lead to delays and complications in product delivery, making the process more cumbersome. Choose a port with a responsive customs team and quick processing times.
Proximity to Your Supplier
If the port is located near your suppliers, you can reduce fuel costs and lower overall shipping expenses. Always consider the distance to your supplier when choosing a port or shipping company.
Ready to start your sea shipping journey from China? Here’s the process you need to follow:
1) Pre-Shipment Phase
Before you ship your products, it’s important to consider the negotiation process and shipping rates. Here’s a breakdown of what needs to be done in the pre-shipment phase:
Negotiating with Suppliers
Set clear agreements and finalize the rates. Don’t hesitate to inquire about shipping options, as some suppliers have partnerships with shipping companies. Often, the cost of shipping is included in the overall price of the goods, which can help you avoid high shipping charges.
Selecting Incoterms
Incoterms define the responsibilities between the buyer and supplier. Some common ones include:
- EXW
- FOB
- CIF
- DAP
- DDP
Incoterms outline compensation for issues like lost goods or shipping delays. Be sure to review and understand the terms before agreeing, and select the one that best suits your shipping needs and minimizes responsibility.
Choosing a Freight Forwarder or Shipping Line
If your supplier doesn’t offer shipping services, it’s time to find your own freight forwarder. Look for the following qualities in your chosen provider:
- Experience and shipping capabilities
- Guarantees for on-time delivery
- Competitive pricing with accessibility to your destination country
- Real-time tracking services to monitor your cargo’s location
2) Booking Process
Now that you’ve selected a freight forwarder, here’s the next step: the booking process.
Requesting Quotes
Get quotes from several shipping carriers to avoid monopolizing with one and possibly driving up costs. Aim for 5-10 carriers to compare prices and services.
Providing Shipment Details
Once you’ve chosen your carrier, you’ll need to send them comprehensive details about your shipment. This includes:
- Shipping location
- Product specifications (weight and volume)
- Contact details (phone number, name, etc.)
Confirming the Booking
Once you’ve provided all the details and agreed on the quote, finalize the terms with the shipping company. It’s best to sign a formal agreement to ensure everything is set and avoid potential complications.
3) Documentation Preparation
For international shipments, proper documentation is essential. Customs will carefully verify your paperwork. The key documents include:
- Commercial Invoice: This document details the product purchase, including description, value, and quantity.
- Packing List: If shipping multiple types of products, list all items and their packaging specifications.
- Bill of Lading: A crucial document issued by the carrier, outlining the type, quantity, and destination of goods.
- Certificate of Origin: A certificate verifying where the products were manufactured. You’ll need this for customs clearance.
- Product-Specific Certificates: Certain items, like electrical products or hazardous materials, require additional certifications (e.g., FCC, CE).
Note: Certification requirements vary by country. For example, the EU requires CE certificates, while the U.S. has its own set of regulations.
4) Cargo Preparation
Once the documentation is in place, it’s time to prepare your cargo for shipping.
Proper Packaging
Packaging is key not only for safety but also for creating a positive unboxing experience for your customers. Here are a few tips for effective packaging:
- Make it branded to promote your business.
- Add extra layers for safety.
- Test packaging materials for moisture resistance and durability.
- Use eco-friendly materials to build consumer trust.
Labeling
Just as important as packaging, labeling should be done correctly to ensure clarity and compliance:
- Use waterproof labels.
- Include your brand logo for better recognition.
- Place labels in clear, visible areas.
Container Stuffing
For LCL (Less than Container Load), costs are based on product weight or volume. In contrast, FCL (Full Container Load) allows for more efficient stuffing. A 20GP FCL container typically holds around 28 cubic meters of goods, a 40GP holds 58 cubic meters, and a 40HQ can accommodate up to 68 cubic meters.
5) Transportation to Port
Where is your departure port? Once you specify the location, maximize your shipping efficiency with the following steps.
Domestic Transportation Arrangements
Coordinate inland transport services, such as trucks or other local delivery systems, to get your products to the port. Typically, the supplier handles this, but it’s important to confirm the logistics.
Delivery to Port of Departure
Pay the necessary shipping fees and confirm the product’s delivery to the port of departure.
6) Export Customs Clearance in China
When shipping to the U.S., China is the export country, while the U.S. is the import country. Customs clearance is required at both import and export points.
Submitting Export Declarations
It’s time to prepare and submit all export documents, such as commercial invoices and bills of lading. These documents are essential for customs clearance.
Obtaining Required Permits
Ensure you obtain the necessary export licenses and permits from customs before shipment. After verification, these documents will allow your goods to proceed.
Customs Inspection
Customs will perform thorough inspections to ensure your products meet safety and regulatory standards. This process is essential for clearing the goods for shipment.
7) Port Handling
Once your products arrive at the port, they undergo several handling steps, including the following:
Container Placement in the Yard
Before shipping, containers are stored in the yard until they are ready to be loaded onto the vessel. During this time, you can track your shipment’s progress.
Insurance
Shipping insurance is critical to protect against unforeseen issues. Select an insurance provider with reliable coverage and fast claim handling.
Loading onto the Vessel
Once the containers are ready, they are loaded onto the vessel for transportation to their final destination.
8) Ocean Transit
The shipping journey from origin to destination begins, following these key steps:
Vessel Departure
The vessel departs on its final voyage. Make sure your goods are insured to protect them during transit.
Tracking the Shipment
Request a tracking ID from your carrier to monitor the real-time location of your shipment during its ocean journey.
Communication with Freight Forwarders
Stay in contact with your freight forwarders to ensure all arrangements are in place for the safe arrival of your goods.
9) Arrival at Destination Port
Upon arrival at the destination port, the following procedures are undertaken:
Vessel Berthing
The ship docks at the port. Once anchored, the unloading process can begin.
Unloading of Cargo
Cargo is offloaded from the vessel and temporarily stored at the port facility while awaiting further transport.
10) Import Customs Clearance
Customs at the destination country will inspect your products. Here’s the process for clearing customs:
Customs Brokers and Their Role
Custom brokers assist in gathering the necessary documents for import clearance. They are invaluable in ensuring smooth processing at customs.
Submitting Import Declarations
Submit your import documents, such as invoices and bills of lading, to the relevant customs authorities.
Paying Duties and Taxes
Import duties and taxes apply to different products, with varying rates depending on the destination country. Additionally, customs fees for inspections may apply.
Customs Inspection
Customs will carry out detailed inspections, such as X-raying the cargo, to ensure it matches the declared details and meets regulations.
11) Final Delivery
Once your goods reach the destination country, the final leg of shipping to your address occurs:
Arranging Inland Transportation
Coordinate local transportation to deliver the products from the port to your doorstep. Typically, this involves truck or trailer delivery services.
Receiving Goods at Final Destination
Ensure someone is available to receive the goods at the final destination. Stay in touch with delivery agents to facilitate a smooth handover.
12) Post-Shipment
Once the products are received, here are the next steps:
Confirming Receipt of Goods
Check the product quantities and condition to ensure they match your expectations.
Handling Claims or Issues
In the case of delayed delivery or damaged goods, contact your supplier to address the issue. Additionally, you can file a claim with your insurance provider for compensation.
Evaluating the Shipping Process
Assess your shipping experience. If everything went smoothly, consider rating your freight forwarder and establishing a long-term partnership for future shipments.
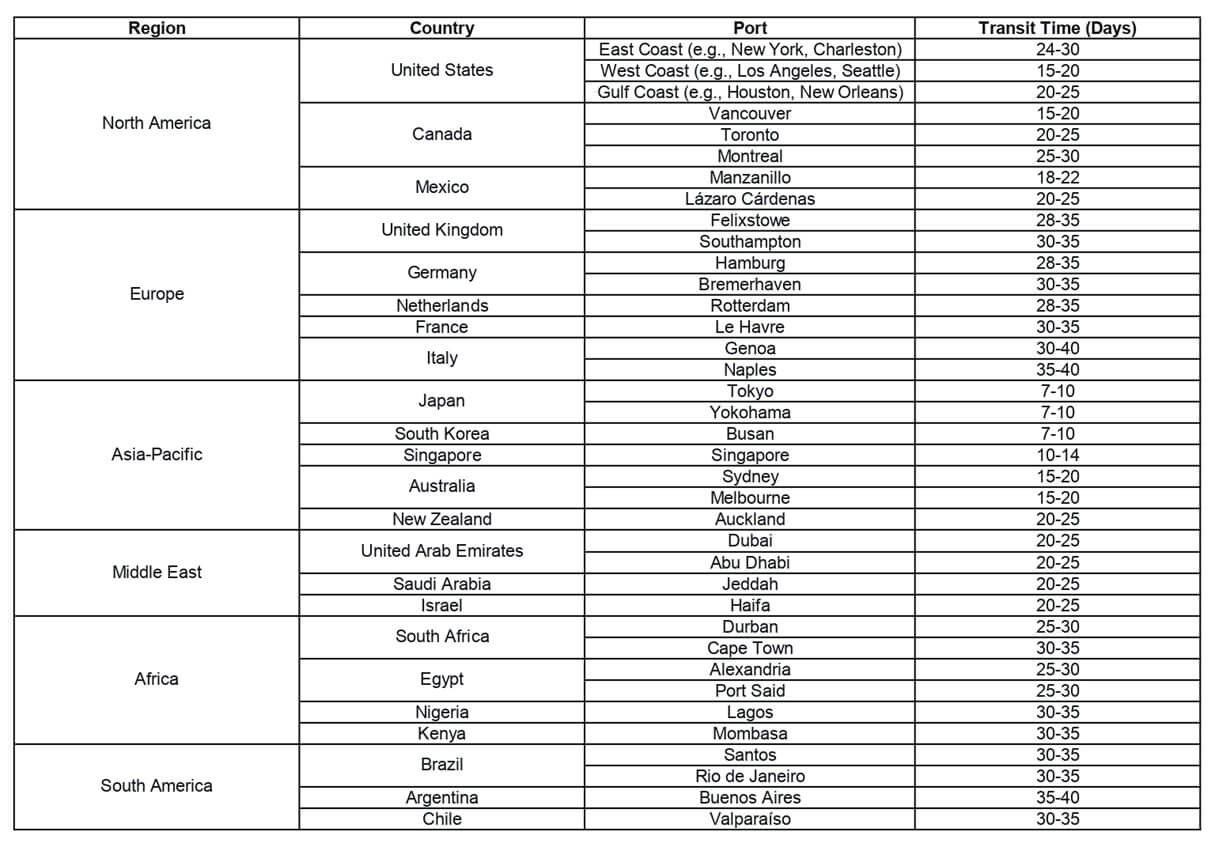
Transit Times for Sea Shipping from China to Other Countries
1) Transit Times to North America
United States
The U.S. is a major importer of goods, with several shipping routes from China. Here are the estimated delivery times to various U.S. coasts:
- East Coast: Shipping takes approximately 24-30 days.
- West Coast: Estimated transit time is 15-20 days.
- Gulf Coast: Typically takes around 20-25 days.
Canada
Shipping times to Canada can vary depending on the destination city:
- Vancouver: Around 15-20 days.
- Toronto: Estimated delivery time of 20-25 days.
- Montreal: Takes approximately 25-30 days.
Mexico
For shipments to Mexico, expect a transit time of at least 25 days.
- Manzanillo: Around 18-22 days.
- Lázaro Cárdenas: Typically 20-25 days.
2) Transit Times to Europe
United Kingdom
The UK experiences slower shipping compared to the U.S. from China:
- Felixstowe: About 28-35 days.
- Southampton: Typically 30-35 days.
Germany
Germany usually has a transit time of around 35 days.
- Hamburg: Takes approximately 28-35 days.
- Bremerhaven: Estimated time is 30-35 days.
Netherlands
Shipping to the Netherlands follows a similar timeline as Germany:
- Rotterdam: Takes about 28-35 days.
France
France generally follows the same shipping schedule:
- Le Havre: Transit time is around 30-35 days.
Italy
For Italy, shipping can take a bit longer:
- Genoa: Usually 30-40 days.
- Naples: Takes approximately 35-40 days.
3) Transit Times to Asia-Pacific
Japan
Japan has one of the fastest shipping times from China, often taking no more than two weeks:
- Tokyo: Around 7-10 days.
- Yokohama: Typically 7-10 days.
South Korea
Shipping to South Korea is also quick, typically around 7-10 days due to its proximity:
- Busan: Takes about 7-10 days.
Singapore
Shipping to Singapore also falls under the fast category, usually within 10-14 days.
Australia
Shipping to Australia is relatively quick as well, with a maximum shipping time of around 20 days:
- Sydney: Typically 15-20 days.
- Melbourne: Estimated time of 15-20 days.
New Zealand
Shipping to New Zealand takes about 20-25 days:
- Auckland: Around 20-25 days.
4) Transit Times to the Middle East
United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The UAE is well-connected to China, making shipping times faster:
- Dubai: Typically 20-25 days.
- Abu Dhabi: Also around 20-25 days.
Saudi Arabia
Shipping from China to Saudi Arabia is fairly quick as well:
- Jeddah: Takes about 20-25 days.
Israel
Shipping to Israel follows a similar timeline:
- Haifa: Around 20-25 days.
5) Transit Times to Africa
South Africa
Shipping to South Africa typically takes about 30 days:
- Durban: Around 25-30 days.
- Cape Town: Estimated time of 30-35 days.
Egypt
Shipping to Egypt also takes about a month:
- Alexandria: Typically 25-30 days.
- Port Said: Around 25-30 days.
Nigeria
Shipping to Lagos, Nigeria, generally takes around 30-35 days.
Kenya
Shipping to Mombasa, Kenya, also takes about 30-35 days.
6) Transit Times to South America
Brazil
Shipping to Brazil generally takes around 35 days:
- Santos: Typically 30-35 days.
- Rio de Janeiro: Around 30-35 days.
Argentina
Argentina is farther from China, leading to slower shipping times:
- Buenos Aires: Estimated time is 35-40 days.
Chile
Shipping to Chile takes a similar amount of time:
- Valparaíso: Typically 30-35 days.
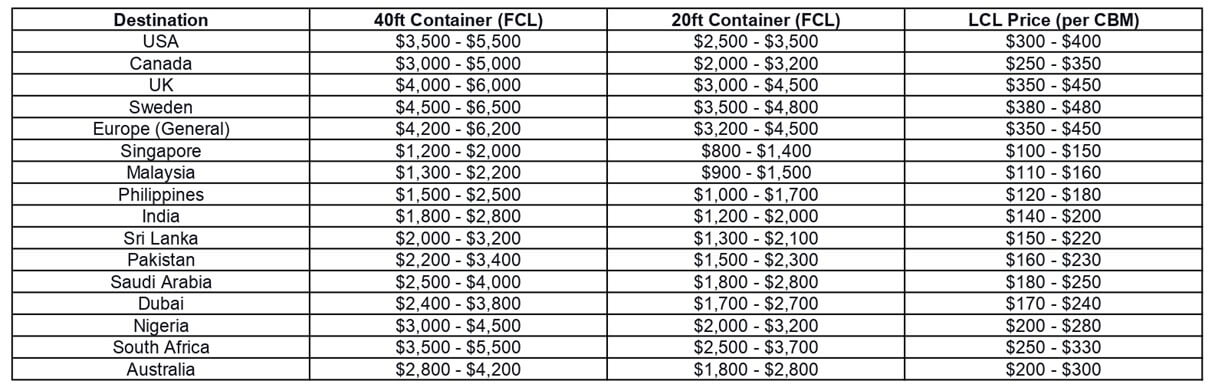
Sea Freight Costs: FCL vs. LCL and Container Types
Sea freight rates vary depending on whether you’re using Full Container Load (FCL) or Less Than Container Load (LCL), and the specific container size also plays a key role in determining costs. Additionally, fluctuating fuel prices and international market rates can impact shipping costs. Below is an overview of the typical sea freight charges for various destinations from China.
1) Sea Freight from China to the USA
Shipping rates from China to the United States depend on the chosen container size and shipping method. The following are the average prices:
- 40ft Container: $3,500 – $5,500
- 20ft Container: $2,500 – $3,500
- LCL Price (per CBM): $300 – $400
2) Sea Freight from China to Canada
Shipping to Canada typically falls between $3,000 and $5,000 USD, but LCL costs may vary by forwarder:
- 40ft Container: $3,000 – $5,000
- 20ft Container: $2,000 – $3,200
- LCL Price (per CBM): $250 – $350
3) Sea Freight from China to the UK
Shipping rates from China to the United Kingdom can go up to $6,000 USD:
- 40ft Container: $4,000 – $6,000
- 20ft Container: $3,000 – $4,500
- LCL Price (per CBM): $350 – $450
4) Sea Freight from China to Sweden
Sweden, being farther from China, tends to have higher shipping costs:
- 40ft Container: $4,500 – $6,500
- 20ft Container: $3,500 – $4,800
- LCL Price (per CBM): $380 – $480
5) Sea Freight from China to Europe
Shipping to Europe generally involves higher costs due to distance, with variations depending on the country:
- 40ft Container: $4,200 – $6,200
- 20ft Container: $3,200 – $4,500
- LCL Price (per CBM): $350 – $450
6) Sea Freight from China to Singapore
Singapore is a closer and more affordable shipping destination:
- 40ft Container: $1,200 – $2,000
- 20ft Container: $800 – $1,400
- LCL Price (per CBM): $100 – $150
7) Sea Freight from China to Malaysia
Shipping to Malaysia is relatively inexpensive due to proximity:
- 40ft Container: $1,300 – $2,200
- 20ft Container: $900 – $1,500
- LCL Price (per CBM): $110 – $160
8) Sea Freight from China to the Philippines
Shipping costs to the Philippines are typically lower compared to other countries:
- 40ft Container: $1,500 – $2,500
- 20ft Container: $1,000 – $1,700
- LCL Price (per CBM): $120 – $180
9) Sea Freight from China to India
As China and India are neighboring countries, shipping is relatively inexpensive and fast:
- 40ft Container: $1,800 – $2,800
- 20ft Container: $1,200 – $2,000
- LCL Price (per CBM): $140 – $200
10) Sea Freight from China to Sri Lanka
Shipping to South Asia, including Sri Lanka, is more affordable than to Europe or the U.S.:
- 40ft Container: $2,000 – $3,200
- 20ft Container: $1,300 – $2,100
- LCL Price (per CBM): $150 – $220
11) Sea Freight from China to Pakistan
As a neighboring country, Pakistan’s shipping costs are on par with Sri Lanka:
- 40ft Container: $2,200 – $3,400
- 20ft Container: $1,500 – $2,300
- LCL Price (per CBM): $160 – $230
12) Sea Freight from China to Saudi Arabia
Shipping to Saudi Arabia is fairly cost-effective due to the short distance:
- 40ft Container: $2,500 – $4,000
- 20ft Container: $1,800 – $2,800
- LCL Price (per CBM): $180 – $250
13) Sea Freight from China to Dubai
Dubai, similar to Saudi Arabia, offers comparable shipping costs:
- 40ft Container: $2,400 – $3,800
- 20ft Container: $1,700 – $2,700
- LCL Price (per CBM): $170 – $240
14) Sea Freight from China to Nigeria
Shipping to Nigeria is in line with costs for other regions:
- 40ft Container: $3,000 – $4,500
- 20ft Container: $2,000 – $3,200
- LCL Price (per CBM): $200 – $280
15) Sea Freight from China to South Africa
Shipping to South Africa is comparable to costs to the U.S. and Europe:
- 40ft Container: $3,500 – $5,500
- 20ft Container: $2,500 – $3,700
- LCL Price (per CBM): $250 – $330
16) Sea Freight from China to Australia
Shipping from China to Australia is relatively expensive due to the distance:
- 40ft Container: $2,800 – $4,200
- 20ft Container: $1,800 – $2,800
- LCL Price (per CBM): $200 – $300
Sea Freight Risks and Challenges
Sea freight comes with a range of risks and difficulties, primarily due to the slower transportation method and the use of multiple containers on a single vessel. These risks are worth considering to avoid potential problems.
Common Shipping Issues
Everyday sea freight operations can face various challenges, such as:
-
Delays in Shipping: Your shipments can be delayed due to vessel handling, port congestion, and other operational factors. This can result in financial losses from increased backorders and unmet delivery deadlines.
-
Product Damage: In Less than Container Load (LCL) shipping, your goods share space with those of other shippers. This can lead to potential damage from shifting cargo or compression within the container.
-
Loss of Goods: Shipping multiple products on the same vessel can lead to confusion, especially if labels are lost or misplaced, causing misrouted or lost shipments.
Seasonal Shipping Challenges
Certain times of the year bring additional risks due to high demand or adverse conditions:
-
Peak Shipping Seasons: During busy seasons, such as holidays or promotional periods, vessels may become overloaded, leading to delays and a backlog of shipments.
-
Weather Conditions: Sea freight is especially susceptible to weather-related delays, with storms, rough seas, and poor visibility potentially affecting sailing schedules.
-
Chinese New Year: National holidays, like Chinese New Year, can disrupt shipping schedules due to factory closures and port congestion.
How to Mitigate Risks in Sea Freight
To minimize delays and maximize efficiency, consider the following strategies:
-
Opt for Consolidated Shipping Services: By combining shipments with others, you can reduce shipping costs and improve overall efficiency.
-
Ship During Off-Peak Seasons: Avoid peak times such as holidays and high-demand periods to reduce the risk of delays and higher costs.
-
Ensure Proper Packaging: Use waterproof labels and unbreakable packaging to protect your goods from damage during transit.
-
Monitor the Shipping Calendar: Stay informed about global events, national holidays, and seasonal patterns that may affect shipping schedules and plan accordingly.
-
Work with Reliable Shipping Partners: Collaborating with trustworthy and efficient shipping companies can help avoid many of these risks, ensuring smoother and faster deliveries.
Choosing a Freight Forwarder: Tips and Red Flags
Navigating the Freight Forwarder Selection Process
When you’re diving into the process of selecting a freight forwarder, don’t worry about the hassle. We’ve got some helpful tips and red flags to guide you. Pay attention to these key factors:
Key Criteria for Selecting a Freight Forwarder
When choosing a freight forwarder, consider the following essential criteria:
- Experience and Expertise: Aim for at least a decade of industry experience.
- Reputation: A strong reputation is vital for ensuring reliable services.
- Global Shipping Networks: A broad network helps facilitate smooth international shipping.
- Technology and Communication: Modern tools and clear communication can streamline the shipping process and reduce concerns.
- Affordability: Look for competitive pricing from reliable freight forwarders.
Important Questions to Ask Potential Freight Forwarders
Before finalizing your choice, make sure to ask these critical questions:
- How long have you been in business?
- What is the typical transit time from China to my destination country?
- Do you offer multiple shipping options for different needs?
- Can you deliver directly to my door?
- How do you maintain transparency in pricing and processes?
- What are your shipping costs to my specific location?
Red Flags to Watch Out For
Before committing to a freight forwarder, be cautious of the following warning signs:
- Poor Communication: If a freight forwarder struggles with clear communication, it could lead to misunderstandings or missed deadlines.
- Negative Reputation: Avoid companies with a history of delays, unfulfilled commitments, or poor customer service.
- Lack of Proven Track Record: New or inexperienced freight forwarders might not have the necessary experience or reliability. Be cautious when considering these options.
- Unrealistically Low Prices: Extremely low rates can sometimes be a red flag, indicating potential scams or poor-quality service. Be wary of deals that seem too good to be true.
Strategies for Streamlining Sea Freight from China
Maximizing Efficiency in Sea Freight from China
To optimize your sea freight shipping from China and ensure smooth operations, consider these effective strategies:
1. Consolidate Shipments
Combining shipments into a single container (LCL or FCL) can significantly reduce shipping costs and improve efficiency. Grouping goods from multiple suppliers or orders can save on space and costs.
2. Plan for Off-Peak Seasons
Shipping during off-peak periods helps avoid delays caused by high demand during busy seasons, such as holidays or peak shipping times. Plan ahead to ensure faster processing and more affordable rates.
3. Choose the Right Container Size
Selecting the appropriate container size (20ft or 40ft) based on your shipment volume can help minimize wasted space and reduce overall freight costs. FCL (Full Container Load) may be more cost-effective for large shipments, while LCL (Less than Container Load) suits smaller volumes.
4. Optimize Packaging
Proper packaging ensures products are safely stored and reduces the risk of damage during transit. Use high-quality, space-efficient packaging to reduce the volume of your shipment, which can also help lower freight costs.
5. Work with Experienced Freight Forwarders
Partnering with a reliable and experienced freight forwarder who understands the complexities of sea freight can save time and money. Their expertise in choosing the best routes, handling paperwork, and managing logistics can streamline the shipping process.
6. Utilize Advanced Tracking Systems
Real-time tracking and advanced logistics software allow you to monitor your shipment’s progress, making it easier to manage delays or issues that may arise during transit. It also helps maintain communication with your freight forwarder.
7. Understand Incoterms
Familiarize yourself with Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) to clarify the responsibilities of both the buyer and seller in terms of delivery, shipping, and risks. This can help you avoid disputes and ensure smooth transit.
8. Leverage Bulk Discounts
If you ship large quantities, consider negotiating with carriers for bulk discounts. Shipping in bulk can provide significant savings on freight costs, especially with regular or long-term shipments.
9. Streamline Customs Documentation
Ensure that all your documents, such as the Bill of Lading, commercial invoices, and packing lists, are accurately prepared and submitted to avoid delays in customs clearance. Proper documentation can speed up the entire shipping process.
10. Focus on Environmental Sustainability
Opt for eco-friendly shipping practices, such as using recyclable packaging or working with carriers that prioritize sustainability. Not only does this benefit the environment, but it can also appeal to customers who value green practices.
Cost Reduction Strategies:
- Reducing Shipping Expenses
Want to reduce shipping expenses? Here are a few tips to help you cut down costs:
-
Opt for FCL (Full Container Load):
While it may seem counterintuitive, FCL can often be more economical, especially for bulk shipments. Shipping a full container can lead to significant cost savings. -
Partner with Cost-Effective Carriers:
Not all carriers offer the same value. Shop around for reliable, budget-friendly providers who can handle your shipments effectively. -
Select Ports Closer to Your Destination:
Choosing ports nearer to your delivery location can help reduce fuel costs, resulting in lower overall shipping fees.
Improving Efficiency:
Enhance shipping efficiency by focusing on:
-
Collaborating with Trusted Shipping Agents:
Reliable agents are key to ensuring timely deliveries and avoiding delays. -
Optimizing Packaging:
Safe, efficient packaging not only ensures your goods arrive intact but also helps reduce shipping space and associated costs. -
Leveraging Technology for Tracking:
Using real-time tracking technology helps ensure orders are monitored, reducing errors and delays. -
Advanced Booking:
Booking shipments ahead of time can avoid last-minute issues and often reduces costs.
Building Strong Relationships:
Fostering long-term partnerships with suppliers and freight providers can lead to:
-
Better Rates:
As you build trust with carriers and suppliers, they may offer you better rates or discounts for repeat business. -
Faster Service:
Strong relationships often result in prioritized services, speeding up the shipping process and reducing waiting times. -
Consistency in Cost and Service:
Stable partnerships help avoid unexpected costs and ensure smoother, more reliable logistics.

